环球教育
2021-05-21首先我们来了解一下到底什么是生物学(biology),the scientific study of the natural processes of living things.
(来源:https://dictionary.cambridge.org/us/dictionary/english/biology)
简单翻译一下就是一种研究生命体自然进程的科学。
而在托福的生物学文章中,其内容通常会提及物种的起源(the origin of species)和进化(evolution),也会针对某个物种的行为去解释原因,以及它们如何适应环境(adapt the environment)、繁殖(reproduce)和自然选择(natural selection)的。那我们就先来看看在“生物”这个大范围下又具体细分为哪些吧。
首先地球上所有的生物都可以被分为植物群(flora)和动物群(fauna),上次植物学(botany)的文章,我们已经介绍过植物相关的单词啦,所以这次重点将会放在动物上面哦。
世界上的动物已知的就有超过百万种,这么庞大的数量会给生物学家(biologist)的工作带来很大的困难,这个时候就要引入分类学(taxonomy)的概念,给动物们分类,那按照分类的标准不同,我们来看看~
按照骨骼的性质划分:
Vertebrate / ˈvɜ:rtɪbrət / n脊椎动物
Invertebrate /ɪn ˈvɜ:rtɪbrət/ n无脊椎动物
(考题7 reading passage1:One question was related to evidence that the invertebrate fauna (animals without spines) of the Mediterranean had changed abruptly about 6 million years ago.)
按照生活环境划分:
Amphibian /æmˈfɪbiən/ n两栖动物
(考题40 reading passage3:In contrast to mammals and birds,amphibians are unable to produce thermal energy through their metabolic activity)
Aquatic /əˈkwætɪk/ adj水生的
(考题44 reading passage1:they had radiated into almost all availableaquatic habitats)
Terrestrial /təˈrestriəl/ adj陆地的;陆栖的;陆生的
(考题44 reading passage1:One of the most significant evolutionary events that occurred on Earth was the transition of water-dwelling fish to terrestrial tetrapods.)
而如果要细分到某一种具体物种的分类,要经过七层划分,请看下图
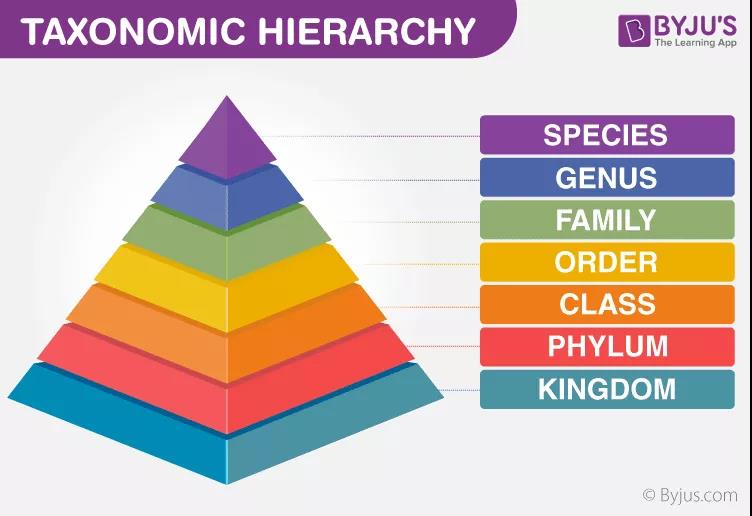
从下到上依次是:
Kingdom /ˈkɪŋdəm/ n界
phylum /ˈfaɪləm/ n门
class /klæs/ n纲
order /ˈɔ:rdə(r)/ n目
family /ˈfæməli/ n科
genus /ˈdʒi:nəs/ n属
species /ˈspi:ʃi:z/ n种
而光知道一个模糊的分类概念,在托福的文章中是远远不够的,因为通常都会涉及到某个具体的物种。要是不知道他们的意思,在阅读或听力中想要把握文章描写对象的详细特点就会比较困难,那么接下来就是一波具体的物种单词啦。
首先是昆虫(insect)类:
Larva /ˈlɑ:rvə/ n幼虫,幼体
Pest /pest/ n害虫,害兽,害鸟
Worm /wɜ:rm/ n蠕虫
两栖动物amphibian:

Turtle /ˈtɜ:rtl/ n龟
Snake /sneɪk/ n蛇
Toad /toʊd/蟾蜍
(考题25 listening lecture1: But the cane toad itself became a pest and has destroyed much of the wildlife on that continent.)
Lizard /ˈlɪzərd/n蜥蜴
(考题21 listening lecture3: Probably back in some previous biology course you learned that snakes evolved from lizards)
Chameleon /kəˈmi:liən/ n变色龙
Crocodile /ˈkrɑ:kdaɪl/ n鳄鱼
水生动物Aquatic animal:
Dolphin /ˈdɑ:lfɪn/ n海豚
Whale /weɪl/ n鲸鱼
Shrimp /ʃrɪmp/ n小虾
Prawn /prɔ:n/ n对虾,大虾,明虾
Lobster /ˈlɑ:b stə(r)/ n龙虾
Crab /kræb/ n螃蟹
Clam /klæm/ 蛤蜊,蚌
Coral /ˈkɔ:rəl; ˈkɑ:rəl/ n珊瑚
(考题27 listening lecture1: And there's another technique that's been experimented with to try to help coral reefs recover from bleaching.)
Seal /si:l/ n海豹
Octopus /ˈɑ:ktəpəs/ n章鱼
(考题17 listening lecture4: The octopus is prey to many species, including humans, so how does it escape its predators?)
Otter /ˈɑ:tər/ n水獭
陆生动物Terrestrial animal:
Gorilla /gəˈrɪlə/ n大猩猩
Chimpanzee /ˌtʃɪmpænˈzi:/ n黑猩猩
Baboon /bæˈbu:n/ n狒狒
Microbe /ˈmaɪkroʊb/ n微生物
(考题53 reading passage2: High moisture and temperatures speed the growth of soil microbes that decompose organic compounds)
Bacteria /bækˈtɪriə/ n细菌
Virus /ˈvaɪrəs/ n病毒
而在生物类的文章中,掌握了具体的描写对象之后,我们还需要把握住它们干了些什么,这些行为带来了什么样的影响,下面就是一波关于生物行为的单词啦,赶紧接住!
Subsist /səbˈsɪst/ v存在,有效/维持度日
Exist /ɪgˈzɪst/ v存在,实际上有/生活,生存
Secrete /sɪˈkri:t/ v分泌
(考题17 reading passage3: The ants live in large, hollow thorns and eat sugarsecreted by the tree.)
Assimilate /əˈsɪməleɪt/ v消化,吸收
Breed /bri:d/ v交配,繁殖/喂养(注意过去式bred,过去分词bred)
Proliferate /prəˈlɪfəreɪt/ v迅速繁殖(或增殖);猛增
Propagate /ˈprɑ:pəgeɪt/ v繁殖;增殖
(考题9 reading passage3: These plants propagate by producing spores–tiny fertilized cells that contain all the instructions for making a new plant–but the spore are unprotected by any outer coating and carry no supply of nutrient.)
Evolve /iˈvɑ:lv/ n进化,演化
(考题39 listening lecture4: Cows and goats have evolved highly specialized digestive systems that allow them to metabolize cellulose.)
Darwinism /ˈdɑ:r wɪnɪzəm/ n达尔文主义(查尔斯·达尔文于 19 世纪创立的学说,认为生物通过自然选择而进化)
Extinct /ɪkˈstɪŋkt/ adj已经毁灭的
Extinction /ɪkˈstɪŋkʃn/ n灭种
那么还是一些相关的单词:
Immune /ɪˈmju:n/ adj有免疫力的
(考题17 reading passage3: In vertebrates, the immune system provides a multiple defense against internal parasites.)
Immunity /ɪˈmju:nəti/ n免疫力
Metabolism /məˈtæbəlɪzəm/ n新陈代谢
(考题23 reading passage1: The city is an extraordinary processor of mass and energy and has its own metabolism)
Morphology /mɔ:rˈfɑ:lədʒi/ n形态学
Microscope /ˈmaɪkrəskoʊp/ n显微镜
Calorie /ˈkæləri/ n卡路里
Glucose /ˈglu:koʊs; ˈglu:koʊz/ n葡萄糖
(考题18 listening lecture4: In frogs, the extra glucose makes it harder for the winter inside the cells to freeze.
Protein /ˈproʊti:n/ n蛋白质
